S/MIME Certificates
Secure sensitive information and identify yourself as a trusted sender.
The S/MIME client certificate allows you to control access and authenticate users’ identities when connecting to platforms and services, as well as encrypt and sign emails to ensure information privacy and verify the sender’s legitimacy.
Without two-factor authentication (2FA) and email and document signing, your organization is as secure as using the password “123.” Client certificates (also known as personal ID certificates) identify and validate individual users. This way, you can control what each user can and cannot access, as well as encrypt and sign the communications they send and receive.
Control access
Allows and restricts access to applications, websites, databases, and devices.
Sign communications
Sign and encrypt emails to protect your organization and recipients from phishing attacks and online fraud.
2FA Activation
Protect your organization from password hacks by adding an extra layer of authentication.

S/MIME Benefits
- Secure log-in for email and internal or external applications.
- Prevent phishing, scamming, and data breaches.
- Identify your users as trusted senders to clients and contacts.
How S/MIME certificates work
Access authentication
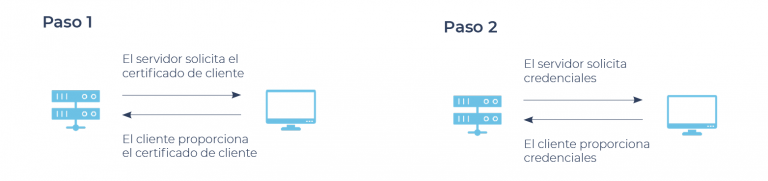
Once the server has been configured for client certificate authentication, it will allow access only if the user presents the corresponding email certificate. Without this certificate, a user attempting to access the server will not be able to view the login page.
Email security
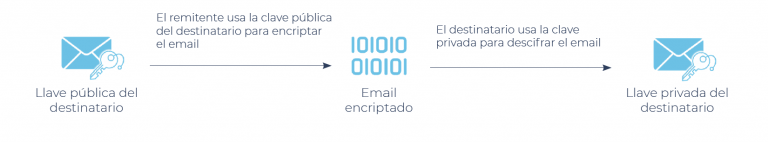
Email client certificates use a public/private key pair. The private key is assigned to a user and is used to “sign” outgoing communications with that user’s unique identity. The public key is used to verify signatures and encrypt incoming messages.
Included features
- Email encryption
- Email signature
- Email Autentication
- Document Signing
Frequently Asked Questions (FaQ)
How does S/MIME certificate work?
S/MINE certificates work through encryption protocols that establish a secure channel between the browser and the server. They verify the identity of the domain and encrypt the transmitted information, preventing interception and tampering. Once issued and installed, the certificates display the padlock icon next to the domain’s URL in the browser, indicating to users that they are browsing securely in accordance with standards defined by the relevant authorities.
Talk with a security expert
We will get back to you as soon as possible